In today’s digital age, where online privacy and security are paramount, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become an essential tool for internet users around the globe. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify VPNs, explaining their purpose, how they work, and why they are critical in maintaining your online privacy and security.
Understanding VPNs
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. The primary purpose of a VPN is to provide privacy and security to data and communications.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of how VPNs work and their key components:
1. What is a VPN?
- Encryption: VPNs encrypt data before it leaves your device, ensuring that it remains secure and private as it travels over the internet.
- Tunneling: A VPN creates a “tunnel” through the internet, protecting the data from external access or inspection.
2. How Does a VPN Work?
- Connection: When you connect to a VPN, your device communicates with a VPN server.
- Data Transmission: Your data is encrypted by your device, sent to the VPN server through the tunnel, and then decrypted by the VPN server.
- IP Address Concealment: The VPN masks your IP address with its own, so your online actions are virtually untraceable.
3. Types of VPNs
- Remote Access VPN: Allows individual users to connect to a private network from a remote location.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Connects entire networks to each other, typically used in corporate environments.
4. Protocols Used in VPNs
- OpenVPN: An open-source protocol known for security and reliability.
- IKEv2/IPsec: Known for strong security and stability, especially good for mobile devices.
- L2TP/IPsec: Combines features of L2TP and IPsec for data encryption.
- WireGuard®: A newer protocol praised for its simplicity and high-speed performance.
5. Uses of VPNs
- Privacy: Hides your browsing activity from your local network and ISP.
- Security: Encrypts data to protect against hackers, especially on public Wi-Fi.
- Accessing Restricted Content: Bypasses geo-restrictions and censorship by masking your IP address.
6. Considerations When Using VPNs
- Speed: VPNs can sometimes slow down your internet connection.
- Legal and Policy Compliance: Ensure compliance with local laws and service provider policies.
- Trustworthy Provider: Choose a reputable VPN provider to avoid malicious practices.
7. Potential Risks
- Free VPN Services: Some may sell your data or show ads.
- Configuration Errors: Incorrect setup can lead to vulnerabilities.
- VPN Blocking: Some services and countries actively block VPN usage.
8. Emerging Trends
- Increased Use in IoT: VPNs are being used for securing Internet of Things devices.
- Cloud VPNs: Integration with cloud services for enhanced security and scalability.
In summary, VPNs are a critical tool for enhancing online security and privacy. Whether for personal use or within an enterprise, understanding the basics of VPN technology helps users make informed decisions about their internet privacy strategies.
Benefits of Using a VPN
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) offers several benefits, particularly in terms of security, privacy, and online freedom.
Here are some of the key advantages:
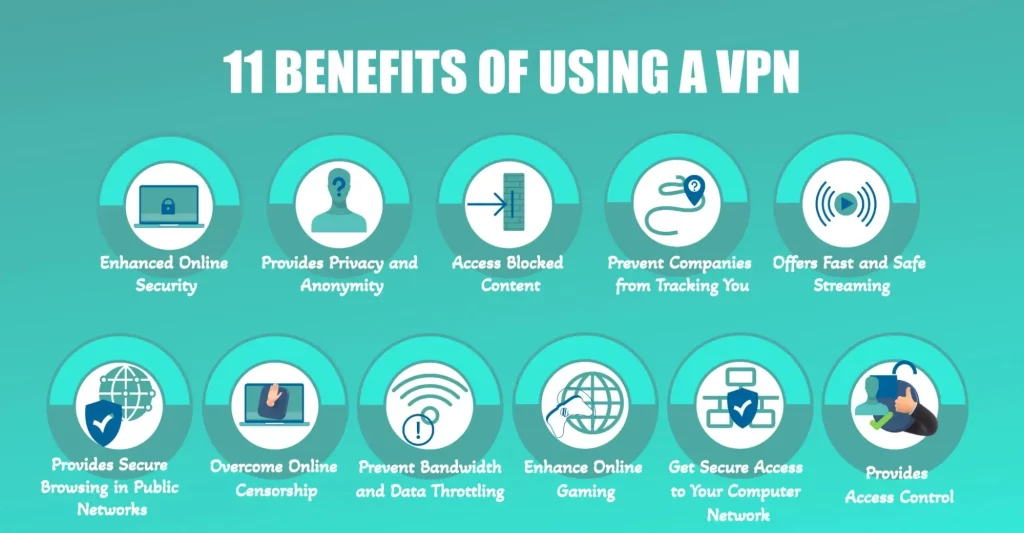
- Enhanced Security: A VPN encrypts your internet connection, which protects your online activities from hackers, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks. This encryption makes it much harder for third parties to intercept and read your data.
- Improved Privacy: By masking your IP address, a VPN makes it more difficult for websites and services to track your online activities and your location. This helps in maintaining your anonymity online.
- Access to Geo-Restricted Content: VPNs allow you to bypass geographical restrictions imposed by websites or streaming services. By connecting to servers in different countries, you can access content that would otherwise be unavailable in your region.
- Safe Online Transactions: For those who often engage in online banking or shopping, a VPN can provide an extra layer of security to protect financial details and personal information.
- Bypassing Censorship: In countries where the internet is heavily censored, VPNs can provide access to a free and open internet, allowing users to bypass government restrictions and access a broader range of information and viewpoints.
- Reduced Online Tracking and Targeted Advertising: Since a VPN hides your IP address and location, it becomes more difficult for advertisers to track your browsing habits and target you with ads.
- Secure Data Transfer: For businesses and individuals who need to transfer sensitive information over the internet, a VPN can provide a secure way to do so.
- Remote Access: VPNs enable users to securely access a private network and share data remotely through public networks. This is particularly useful for remote workers.
- Avoidance of Bandwidth Throttling: ISPs sometimes throttle bandwidth on certain types of content or during particular times of the day. A VPN can help avoid this throttling since the ISP cannot see what kind of content you’re accessing.
- Improved Performance: In some cases, using a VPN can result in better internet bandwidth and efficiency. This is not always the case, but it can be a side benefit in certain network configurations.
- Network Scalability: For businesses, VPNs can be a cost-effective way to create a large secure network. The internet’s infrastructure makes it easier to scale a VPN than to build out a private network with the same level of access and security.
Not all VPNs offer the same level of service, security, and privacy, and some free VPNs might even compromise your security instead of enhancing it.
Choosing the Right VPN
Choosing the right VPN (Virtual Private Network) is crucial for ensuring your online privacy and security. Here are several key factors to consider:
- Privacy and Logging Policy: Ensure the VPN has a strict no-logging policy. This means they don’t keep records of your online activities.
- Security Features: Look for strong encryption standards (like AES-256), a kill switch (which stops internet traffic if the VPN disconnects unexpectedly), and protection against DNS leaks.
- Server Locations: More server locations mean more options for geo-spoofing (appearing as if you’re in another country). This is important for bypassing geo-restrictions on content.
- Speed and Performance: VPNs can slow down your internet connection. Look for one with high-speed servers and unlimited bandwidth.
- Ease of Use: The VPN should have a user-friendly interface and be easy to install and configure.
- Compatibility: Ensure the VPN is compatible with all your devices and operating systems.
- Customer Support: Good customer support (like 24/7 live chat) is important for troubleshooting any issues.
- Price: Compare pricing plans. Cheaper isn’t always better. Consider the value for the price, including the number of simultaneous connections allowed.
- Trial Periods and Money-Back Guarantees: A trial period or money-back guarantee is helpful to test the service before committing.
- Reputation: Research user reviews and expert opinions. A trustworthy VPN should have a solid reputation for reliability and customer service.
- Additional Features: Some VPNs offer extra features like ad blocking, malware protection, or dedicated IP addresses.
- Jurisdiction: Consider where the VPN company is based, as this can affect how it handles your data. Countries with stringent privacy laws are generally preferable.
Remember, no VPN offers complete anonymity and it’s important to abide by laws and regulations regarding internet use in your country. Additionally, using a VPN for illegal activities is not advisable and is typically against the VPN provider’s terms of service.
Potential Drawbacks
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are widely used for enhancing privacy and security online. However, they also come with potential drawbacks:
- Slower Internet Speeds: VPNs can slow down internet speeds because they route your traffic through an additional server, which can be far away or congested. The level of encryption also plays a role in reducing speed.
- Security Risks: While VPNs are meant to enhance security, they’re not infallible. Some VPNs might have vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Free or less reputable VPNs might not offer adequate security, making them susceptible to breaches.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: In some countries, the use of a VPN is restricted or illegal. Users might inadvertently break laws or terms of service agreements by using a VPN to access geo-blocked content.
- Cost: Quality VPN services typically require a subscription fee. Free VPNs might exist, but they often have limitations or may compromise your privacy by tracking and selling your data.
- Limited Access to Local Content: While a VPN can provide access to geo-restricted content, it can also block access to local content or websites that might restrict VPN traffic.
- Complexity for Average Users: Setting up and using a VPN can be complex for non-tech-savvy users. Incorrect configuration can lead to vulnerabilities or a false sense of security.
- Potential for Data Logging: Some VPN providers may log user activity. Choosing a provider that maintains a strict no-logging policy is important for privacy, but users must trust the provider to adhere to its policies.
- Device Compatibility and Connection Issues: Some devices may not support VPN software, and others may have difficulty maintaining a stable connection, especially on mobile networks or with certain types of internet connections.
- Trust Factor: You must trust your VPN provider as you’re routing all your internet traffic through them. If the VPN provider is compromised or malicious, your data could be at risk.
- Impact on Online Services: Some online services detect and block VPN traffic. This can prevent access to certain services or result in a less personalized or less efficient user experience.
- Interference with Local Networking: VPNs can interfere with local network settings and make it difficult to access local devices like printers or file servers.
- Latency in Real-Time Applications: VPNs can increase latency, which can be problematic for real-time applications like gaming or video conferencing.
It’s important to weigh these potential drawbacks against the benefits of using a VPN, and if you decide to use one, choose a reputable service that aligns with your specific needs and concerns.



