In an era where digital transformation is not just a trend but a necessity, the shift towards cloud computing has been rapid and decisive. However, with this shift comes a new range of security challenges. The evolving cyber threat landscape poses significant risks to cloud-based systems, making cloud security a top priority for businesses and organizations worldwide.
In this article, we delve into the importance of cloud security in today’s digital age, exploring the current threats and offering insights into effective strategies to mitigate these risks.
Understanding the Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape
Cyber threat landscape is crucial for organizations, governments, and individuals alike. As technology advances, so do the tactics and tools used by cybercriminals.
Rise of Sophisticated Malware and Ransomware
- Advanced Malware: Malware has become more sophisticated, with capabilities like evasion techniques, polymorphism, and exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Ransomware Evolution: Ransomware attacks have evolved from simple lockout schemes to sophisticated multi-stage operations that involve data theft and extortion.
2. Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
- Targeted Phishing: Spear phishing and whaling attacks are more targeted and believable, often using personal information to deceive.
- Social Engineering Tactics: Attackers are using more refined social engineering tactics to manipulate users into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
3. State-Sponsored Cyber Attacks
- Cyber Warfare: Nations are increasingly using cyber capabilities for espionage, sabotage, and influencing foreign affairs.
- Election Interference: There is growing concern about cyber operations aimed at influencing elections and political processes.
4. Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
- Expanding Attack Surface: The proliferation of IoT devices has significantly expanded the attack surface.
- Inadequate Security: Many IoT devices lack strong security features, making them easy targets for hackers.
5. Cloud Security Challenges
- Data Breaches: As more data moves to the cloud, breaches can have far-reaching consequences.
- Misconfiguration: Cloud environments are complex and misconfigurations can lead to significant vulnerabilities.
6. Supply Chain Attacks
- Software Supply Chain: Attackers are targeting software supply chains to compromise multiple victims through a single breach (e.g., SolarWinds attack).
- Hardware Tampering: Concerns about hardware sourced from potentially untrustworthy suppliers.
7. AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
- AI in Cyber Attacks: The use of AI by attackers to automate tasks, personalize phishing emails, and develop more sophisticated malware.
- AI for Defense: Leveraging AI for threat detection, predictive analytics, and automating security responses.
8. Privacy Concerns and Regulations
- Data Privacy Laws: Increasingly stringent data privacy laws (like GDPR) are impacting how organizations handle data security.
- Compliance Challenges: Ensuring compliance with a growing body of regulations is increasingly complex.
9. Mobile Device Vulnerabilities
- Mobile Targeting: Increased targeting of mobile devices with malware, spyware, and exploits.
- BYOD Policies: Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies can introduce additional risks if not properly managed.
10. Insider Threats
- Malicious Insiders: Employees with access to sensitive information can pose significant risks.
- Accidental Breaches: Unintentional actions by employees can also lead to security breaches.
Staying Ahead
- Continuous Education: Regular training on the latest threats and best practices.
- Investing in Security: Prioritizing cybersecurity in IT budgets.
- Proactive Measures: Implementing proactive measures like regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
- Incident Response Planning: Having a robust incident response plan in place.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Modern IT
How Cloud Computing and IoT are reshaping different areas
Role of Cloud Security
The role of cloud security encompasses a range of practices, technologies, policies, and controls deployed to protect data, applications, and the associated infrastructure of cloud computing.
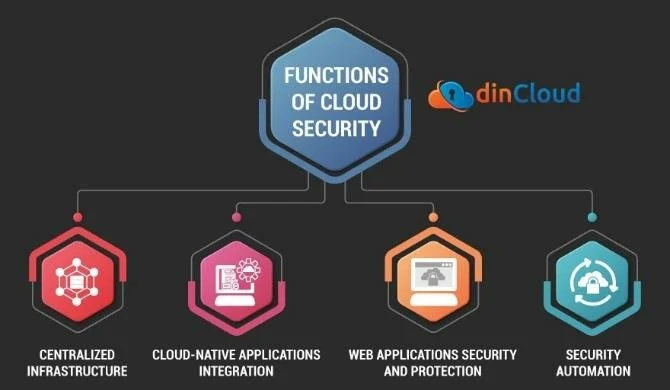

- Data Protection: One of the primary roles of cloud security is to protect data from unauthorized access, theft, or other types of breaches. This involves encryption of data both at rest and in transit, implementing strong access controls, and ensuring regular data backups.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Proper IAM ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources in the cloud. This includes managing user identities, permissions, and roles, and often involves multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO) solutions.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Cloud services often need to comply with various industry and government regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, etc. Cloud security measures must ensure that data handling and processing meet these regulatory requirements.
- Threat Detection and Mitigation: Continuous monitoring of cloud environments is crucial to detect and respond to threats like malware, ransomware, DDoS attacks, and other cyber threats. Advanced security solutions may employ AI and machine learning to detect anomalies and potential threats.
- Network Security: This involves securing the underlying network infrastructure, including protection against unauthorized intrusion and ensuring secure communication channels. This can involve firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Application Security: Ensuring the security of applications running in the cloud is vital. This includes regular vulnerability assessments, patch management, and implementing secure coding practices.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud security also involves planning and implementing strategies for data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity to ensure minimal downtime and data loss in the event of a disaster or cyber attack.
- Physical Security: While often the responsibility of the cloud service provider, physical security of data centers and infrastructure is also a key component. This includes protection against physical theft, damage, and other risks.
- End-user Education and Awareness: Training users about security best practices, phishing threats, and safe data handling is an essential part of maintaining a secure cloud environment.
- Shared Responsibility Model: In cloud computing, security is often a shared responsibility between the cloud service provider and the customer. The provider is typically responsible for securing the infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their data and applications.
Best Practices for Enhancing Cloud Security
Enhancing cloud security is essential in today’s digital landscape, where data breaches and cyber threats are increasingly common.
Here are some best practices for enhancing cloud security:
- Understand the Shared Responsibility Model: In cloud computing, security is a shared responsibility between the cloud service provider (CSP) and the customer. Understand what security aspects are managed by the CSP and what falls under your responsibility.
- Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM):
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
- Employ least privilege access principles, ensuring users have only the access necessary for their role.
- Regularly review and audit user permissions and access rights.
- Data Encryption:
- Encrypt data in transit and at rest.
- Manage encryption keys securely, using hardware security modules (HSMs) or managed key services when possible.
- Consider application-level encryption for sensitive data.
- Secure APIs: Ensure APIs interacting with your cloud services are secured and monitored. Implement API gateways and use OAuth, OpenID Connect, or other robust authentication mechanisms.
- Network Security:
- Use firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs) to secure your network.
- Segment networks to limit lateral movement in case of a breach.
- Regularly perform vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
- Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks: Regularly audit your cloud environments against industry standards and compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, etc.
- Implement Robust Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans:
- Regularly back up data and test restoration processes.
- Have a well-documented disaster recovery plan that is regularly updated and tested.
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response:
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools for real-time monitoring and alerts.
- Have a defined incident response plan and team in place.
- Educate and Train Employees: Conduct regular training sessions on security best practices and awareness. Ensure all employees understand the importance of security and their role in maintaining it.
- Keep Systems and Software Updated: Regularly update all systems, applications, and dependencies to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools: Implement CSPM tools to automate the detection and remediation of risks across cloud environments.
- Secure Endpoints: Ensure that all devices accessing the cloud environment are secure and have up-to-date security software.
- Consider Cloud-Native Security Tools: Utilize security tools that are specifically designed for cloud environments, leveraging their scalability and integration capabilities.
- Vendor Risk Management: Assess the security posture of third-party vendors and integrate them into your overall security strategy.
- Regularly Review and Update Security Policies: Cloud environments evolve rapidly, so it’s crucial to review and update security policies regularly to adapt to new threats and changes in the cloud landscape.
- Identify a geographic region from which a computer is connecting to the internet
- The foundation of the internet rests on the development of crucial communication protocols
Future of Cloud Security
Future of cloud security is a rapidly evolving field, shaped by the changing landscape of cloud computing and the evolving threats that target it
- Advanced Threat Detection and Response: Enhanced capabilities for detecting and responding to threats in real time, using AI and machine learning algorithms to identify unusual patterns and potential breaches more quickly.
- Improved Identity and Access Management (IAM): Stronger focus on IAM, with multi-factor authentication, zero trust models, and just-in-time privileges becoming standard to limit the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Privacy and Sovereignty: Growing importance of data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA will drive the need for improved data handling practices, including data residency and sovereignty considerations.
- Encryption and Data Security: Enhanced encryption techniques both at rest and in transit, and increased use of encryption keys management solutions to protect sensitive data.
- Serverless and Container Security: As more organizations adopt serverless architectures and containerization, security strategies will need to adapt to these new paradigms, focusing on container orchestration tools and serverless function security.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments: Security strategies will evolve to manage the complexities of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, ensuring consistent security postures across various platforms and services.
- Compliance and Regulatory Challenges: Continued evolution in compliance requirements and regulatory frameworks will necessitate more robust compliance management tools and practices in the cloud.
- Edge Computing Security: As edge computing grows, so does the need to secure data processed at the edge of the network, especially in IoT applications, requiring new security protocols and practices.
- Automated Security and Compliance Auditing: Increased use of automation in monitoring, reporting, and auditing to maintain compliance and security standards, reducing human error and improving response times.
- Human Factor and Training: Continued emphasis on training and awareness programs for employees and users, as human error remains a significant vulnerability in cloud security.
- Blockchain for Security: Potential use of blockchain technology for enhancing security in cloud environments, especially in areas like identity verification and secure, transparent transactions.
- AI and ML in Cybersecurity: Leveraging AI and ML for predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and automated threat intelligence to stay ahead of emerging security threats.
- Quantum Computing and Security: Preparing for the impact of quantum computing on encryption and cybersecurity, developing quantum-resistant encryption methods.
- Sustainable and Green Cybersecurity: Incorporating environmental considerations into cybersecurity strategies, balancing digital security needs with energy efficiency and sustainability goals.
These aspects underscore a dynamic and complex environment where cloud security strategies must be continuously adapted to address new technologies, evolving threats, and changing regulatory landscapes.



