Introduction
In an age dominated by technology and interconnectedness, safeguarding your online presence is paramount. As we traverse the vast cyber frontier, the importance of implementing robust strategies for personal online security cannot be overstated.
Stay Informed: Knowledge is Power
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving landscape of the digital world, the phrase “Knowledge is Power” holds more truth than ever before. As we navigate the intricate pathways of the cyber frontier, staying informed emerges as the cornerstone of personal online security.
The Dynamic Nature of Cybersecurity
The realm of cybersecurity is dynamic, with new threats and vulnerabilities surfacing regularly. To effectively protect yourself in this digital age, it is crucial to stay abreast of the latest developments, emerging technologies, and security trends. Ignorance, in this case, is not bliss; it’s a vulnerability waiting to be exploited.
Subscribing to Cybersecurity Resources
One of the most effective ways to stay informed is by subscribing to reputable cybersecurity resources. Numerous blogs, websites, and online platforms are dedicated to providing up-to-date information on the latest security threats, best practices, and insights from industry experts. Regularly checking these sources ensures that you are well-equipped with the knowledge needed to counteract evolving cyber threats.
Following Industry Experts
In the vast landscape of cyberspace, there are experts and thought leaders who dedicate themselves to unraveling the complexities of cybersecurity. Following these professionals on social media platforms provides a direct line to timely information, expert opinions, and valuable tips. Engaging with their content can enhance your understanding of cybersecurity and empower you to make informed decisions.
Participation in Online Forums
Forums and discussion groups focused on cybersecurity are virtual hubs where individuals share experiences, insights, and solutions. Actively participating in these forums allows you to learn from the experiences of others, stay updated on the latest threats, and seek advice from the community. It’s a collaborative approach to fortifying your digital defenses.
Continuous Learning: A Cybersecurity Imperative
The digital landscape is not static, and neither should your knowledge be. Embrace a mindset of continuous learning. Attend webinars, online courses, and workshops dedicated to cybersecurity. Investing time in expanding your knowledge base ensures that you remain ahead of potential threats, equipped with the tools to protect your online presence effectively.
Empowering Yourself for the Digital Journey
In conclusion, staying informed is not merely a suggestion; it is an imperative for anyone navigating the cyber frontier. Knowledge empowers you to recognize potential threats, understand security protocols, and make informed choices that fortify your digital well-being. As the digital world continues to advance, let knowledge be your guiding light through the intricate pathways of the cyber frontier.
Strong Passwords: The Gatekeepers of Your Digital World
In an era where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the digital realm, crafting strong passwords emerges as the first line of defense against potential cyber threats. These alphanumeric combinations act as the gatekeepers to our digital world, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring the integrity of our online presence.
The Anatomy of a Strong Password
A strong password is more than just a random assortment of characters; it’s a carefully constructed key designed to withstand cyber attacks. Here are key elements to consider when creating robust passwords:
- Length Matters: Opt for lengthy passwords. The longer the password, the more challenging it becomes for malicious actors to crack. Aim for a minimum of 12 characters, combining letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Complexity is Key: Integrate a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols into your password. This complexity exponentially increases its resilience against brute-force attacks.
- Avoid Predictable Patterns: Steer clear of easily guessable information such as birthdays, names, or common words. Cybercriminals often employ sophisticated algorithms that can quickly decipher predictable patterns.
- Unique for Each Account: Resist the temptation to reuse passwords across multiple accounts. Each platform should have its distinct, strong password. This prevents a security breach on one platform from compromising others.
Password Managers: Simplifying Security
Managing a myriad of complex passwords can be daunting, but password managers come to the rescue. These tools generate, store, and autofill strong passwords for your various accounts, eliminating the need to remember them all. By using a reputable password manager, you not only enhance security but also streamline the user experience.
Regular Password Updates
Periodically changing your passwords adds an extra layer of security to your digital accounts. Set a schedule to update passwords, especially for critical accounts like email, banking, and social media. This practice minimizes the risk of prolonged exposure to potential threats.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an Extra Layer of Security
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication
These factors typically fall into three categories:
- Something You Know: This is the traditional password or PIN that users create.
- Something You Have: This involves a physical device, often a smartphone or a security token, which generates a unique code or receives a push notification.
- Something You Are: This refers to biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
Enhancing Security Beyond Passwords
The primary advantage of 2FA lies in its ability to mitigate the risks associated with compromised passwords. Even if malicious actors manage to obtain your password, they would still require the second authentication factor to gain access. This dynamic adds a crucial extra layer of protection, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
- Time-Based One-Time Passwords (TOTP): Generated by authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy, these codes change at regular intervals, providing a time-sensitive layer of security.
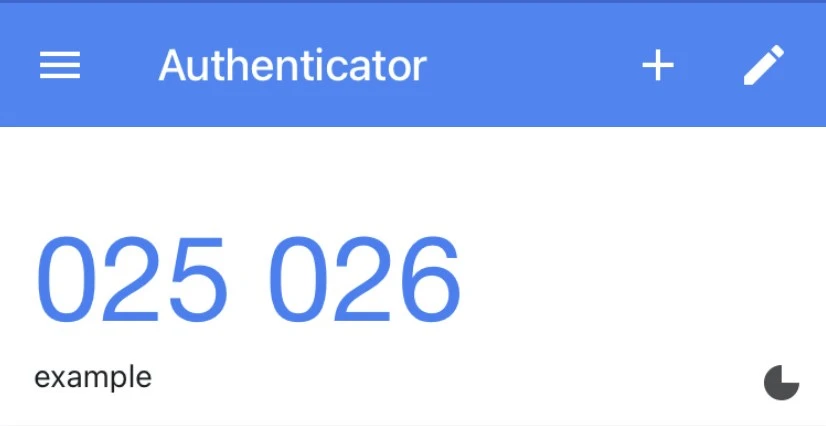
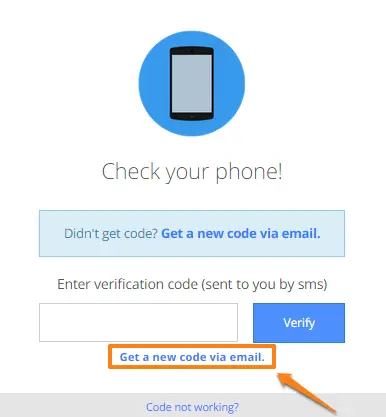
2. SMS or Email Codes: A unique code is sent to the user’s mobile device or email, serving as the second authentication factor.
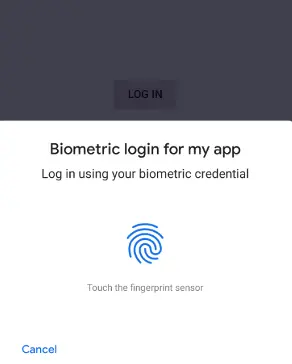
3. Biometric Authentication: Utilizing fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or other biometric data adds a highly secure and convenient layer to the authentication process.
Implementing 2FA Across Platforms
Numerous online platforms, including social media, email services, and financial institutions, offer 2FA as an additional security feature. Enabling 2FA is typically a straightforward process, involving the setup of a secondary authentication method.
Secure Your Wi-Fi Network: Fortify the Digital Perimeter
In the age of seamless connectivity, where our digital lives are intricately woven into the fabric of the internet, securing your Wi-Fi network becomes a paramount step in fortifying the digital perimeter of your home or office. Your Wi-Fi network is not just a gateway to the online world; it is a crucial line of defense that, when fortified, can shield you from potential cyber threats. This article explores the importance of securing your Wi-Fi network and provides actionable steps to fortify the digital perimeter of your connected space.
Understanding the Risks
An unsecured Wi-Fi network is akin to leaving the front door of your digital home wide open to cyber intruders.
Unauthorized access to your network can lead to a plethora of security issues, including:
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors can infiltrate your network, gaining access to sensitive information and compromising your privacy.
- Data Interception: Unencrypted Wi-Fi signals can be intercepted, allowing cybercriminals to eavesdrop on your online activities and potentially steal sensitive data.
- Malware Distribution: An insecure Wi-Fi network provides an avenue for the distribution of malware, infecting connected devices and wreaking havoc on your digital ecosystem.
Actionable Steps to Secure Your Wi-Fi Network
- Change Default Credentials: The default usernames and passwords that come with your router are often well-known to hackers. Change these credentials to unique and robust combinations to enhance security.
- Use Strong Encryption: Enable WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) or, at the very least, WPA2 encryption on your Wi-Fi network. This encrypts the data transmitted between your devices and the router, making it significantly more challenging for attackers to decipher.
- Update Router Firmware: Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch any vulnerabilities and ensure it is equipped with the latest security features.
- Unique Network Name (SSID): Avoid using default or easily identifiable SSIDs. Create a unique network name that doesn’t disclose personal information, making it harder for potential attackers to target your network.
- Password Protect Your Network: Set a strong password for your Wi-Fi network. Combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols to create a robust passphrase that is not easily guessable.
- Enable Network Encryption: If possible, enable network-level encryption, such as a virtual private network (VPN), for an additional layer of protection, especially when accessing sensitive information online.
- Guest Network: Set up a separate guest network for visitors. This segregates your primary network from potential threats and ensures that guests don’t have access to sensitive devices or information.
- Regularly Check Connected Devices: Keep an eye on the devices connected to your network. If you notice any unfamiliar or suspicious devices, investigate and take appropriate action.
Conclusion
Securing your Wi-Fi network is not just a precautionary measure; it is a proactive step toward fortifying the digital perimeter of your connected world. By implementing these actionable steps, you not only protect your personal information but also contribute to a safer online environment. In a world where connectivity is key, securing your Wi-Fi network is the foundation for a resilient and fortified digital presence.



