The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly evolving technology that is reshaping how we interact with the world around us. By integrating internet connectivity into everyday objects, IoT devices offer unprecedented levels of control, efficiency, and data collection. This article delves into the current state of IoT, explores its potential future implications, and discusses the challenges and opportunities it presents.
Understanding the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects — “things” — that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. These devices range from ordinary household items to sophisticated industrial tools.
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects of IoT:
Components of IoT
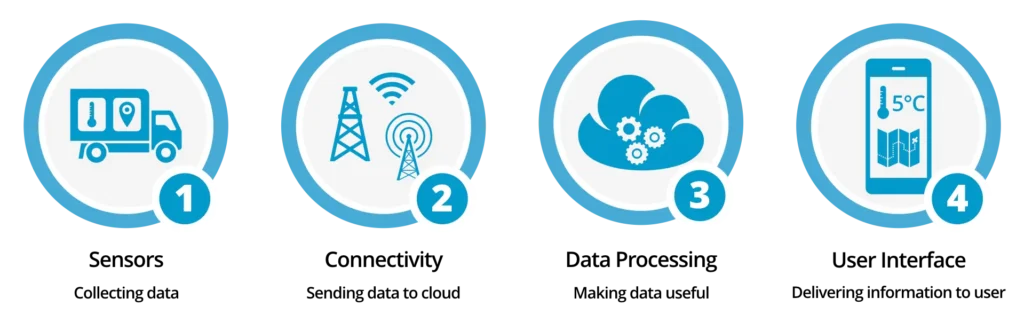
- Devices/Sensors: Devices or sensors collect data from their environment. This could be as simple as a temperature reading or as complex as a full video feed.
- Connectivity: Devices need to connect to the cloud to send and receive data. This can be done through various means such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, etc.
- Data Processing: Once the data is collected and sent to the cloud, software processes it and decides what actions to take.
- User Interface: The end-user needs to interact with the IoT system, often through an application or a dashboard, to receive insights or manipulate the devices.
2. Applications of IoT
- Smart Homes: IoT devices in home automation like smart thermostats, smart locks, and smart refrigerators.
- Wearables: Devices like fitness bands and smartwatches that monitor personal health and fitness.
- Smart Cities: IoT can be used for traffic management, waste management, and energy use optimization in cities.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industries, IoT devices are used for monitoring and optimizing manufacturing and industrial processes.
- Healthcare: IoT devices for patient monitoring, managing inventory, and creating more efficient healthcare systems.
3. Benefits of IoT
- Efficiency: Automation and optimization of tasks can lead to more efficient use of resources.
- Data-Driven Insights: Large amounts of data collected can lead to better decision-making.
- Improved Quality of Life: In areas like healthcare and smart homes, IoT can greatly improve living standards.
4. Challenges in IoT
- Security: With many interconnected devices, the risk of data breaches and hacking increases.
- Privacy: The collection and analysis of personal data raise significant privacy concerns.
- Interoperability: The ability of IoT systems and devices from different manufacturers to work together.
- Scalability: Managing the exponential growth in IoT devices and the data they generate.
5. Future of IoT
- Edge Computing: Processing data on local devices rather than in a centralized cloud to improve speed and reduce latency.
- AI Integration: Using AI to make IoT devices smarter and more adaptive.
- 5G Networks: Will enable faster and more reliable IoT connections.
- Smart Cities and Autonomous Vehicles: IoT will be pivotal in the development of smart urban environments and transportation systems.
6. Ethical Considerations
- Data Rights: Determining who owns the data collected by IoT devices and how it can be used.
- Environmental Impact: The production, use, and disposal of billions of IoT devices pose environmental challenges.
Current State of IoT
As of my last update in April 2023, the “Current State of IoT” (Internet of Things) can be summarized in the following key points:
- Widespread Adoption: IoT devices are now ubiquitous, with significant penetration in sectors like home automation, healthcare, agriculture, and industrial applications.
- Advancements in Technology: Improved sensors, more efficient and cheaper chipsets, and advancements in AI and machine learning have greatly enhanced IoT capabilities.
- 5G Integration: The rollout of 5G technology has provided faster and more reliable connections for IoT devices, enabling more complex applications and real-time data processing.
- Enhanced Security Measures: As IoT devices have become more prevalent, there’s been an increased focus on security. This includes better encryption, secure booting, and regular firmware updates to protect against hacking and other cyber threats.
- Increased IoT in Healthcare: The use of IoT in healthcare, such as remote monitoring devices and wearable health tech, has grown, partly accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Smart Cities Growth: IoT technology is a cornerstone of smart city initiatives, improving urban services like traffic management, waste management, and energy use.
- Energy Efficiency: IoT devices are increasingly used for energy management in both residential and industrial sectors, leading to more efficient energy use and reduced environmental impact.
- Edge Computing Proliferation: There’s been a move towards edge computing in IoT, where data processing happens closer to the IoT device, reducing latency and bandwidth use.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Efforts are being made to improve interoperability between different IoT systems and devices, although this remains a challenge.
- IoT in Retail and Supply Chain: IoT is being increasingly employed in the retail sector for inventory management, and in supply chains for tracking and logistics.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The proliferation of IoT devices has raised concerns about data privacy and the potential for misuse of personal information.
- AI and IoT Convergence: AI is being more tightly integrated with IoT to enable more intelligent and autonomous systems, such as predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
- Growth in Consumer IoT: There is a continuous rise in consumer IoT products like smart home devices, wearables, and personal assistants.
- Investment and Market Growth: The IoT market continues to grow, attracting significant investments from both private and public sectors.
- Challenges in Scalability and Management: As IoT networks grow, challenges related to the scalability and management of these vast networks of devices persist.
- Sustainability and IoT: There is an increasing focus on using IoT for sustainability efforts, such as monitoring environmental conditions and optimizing resource use.
- Regulations and Standards Development: Governments and international bodies are working on developing regulations and standards to guide the safe and ethical use of IoT technology.
- Please note that the IoT landscape is rapidly evolving, and new developments might have emerged after my last update.
Key Benefits of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) brings numerous benefits across various sectors.
Here are key benefits:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: IoT devices can automate and optimize tasks, leading to more efficient use of resources and higher productivity in manufacturing, agriculture, and other industries.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: IoT enables the collection and analysis of real-time data. This helps in informed decision-making, predictive maintenance, and better understanding of customer behavior.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Tracking: IoT is crucial for monitoring systems and environments. This includes everything from tracking inventory in warehouses to monitoring vital signs in healthcare settings.
- Energy Savings: Smart IoT devices can significantly reduce energy consumption by optimizing the use of resources like electricity and water.
- Improved Safety and Security: IoT devices can enhance security systems and monitor environments for safety hazards, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing emergency response.
- Remote Control and Automation: IoT allows for the remote control of devices and systems, leading to automation in homes, industries, and urban infrastructure.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: In the retail and service sectors, IoT helps in providing personalized experiences to customers, improving engagement and satisfaction.
- Cost Reductions: By optimizing operations and maintenance, IoT can help reduce costs over time. This includes reducing downtime in industrial settings and lowering energy costs.
- Healthcare Advancements: IoT in healthcare enables remote monitoring of patients, improved diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans, leading to better health outcomes.
- Smart Cities and Infrastructure: IoT contributes to the development of smart cities, improving traffic management, waste management, and energy use, making urban living more efficient and sustainable.
- Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization: IoT enhances visibility and control over supply chains, improving inventory management, tracking, and logistics.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT devices play a crucial role in monitoring environmental parameters like air quality, water quality, and soil conditions, aiding in conservation efforts.
- Agricultural Improvements: In agriculture, IoT can optimize crop yields, manage resources more efficiently, and monitor livestock health.
- Enhanced Connectivity: IoT connects various devices and systems, leading to better coordination and information exchange across different platforms.
- Innovation and New Opportunities: IoT drives innovation and creates new business models and opportunities across different sectors, from tech startups to traditional industries.
Future Implications of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming our world, and its future implications are vast and multifaceted. By 2024, the IoT landscape has likely evolved significantly, with an ever-growing number of devices connected to the internet, ranging from household appliances to industrial machinery, and from wearable tech to city infrastructure.
Here’s a look at some potential future implications of IoT:
- Smart Cities and Urban Planning: IoT is a key driver in the development of smart cities. Sensors can monitor everything from traffic patterns to air quality, leading to more efficient public transportation, better resource management, and improved quality of life for residents.
- Healthcare Revolution: IoT in healthcare could lead to more personalized and preventive care. Wearable devices can monitor vital signs in real-time, alerting healthcare providers to potential health issues before they become serious. Remote monitoring and telehealth could become the norm, making healthcare more accessible.
- Agricultural Efficiency: IoT applications in agriculture can lead to precision farming, where sensors monitor soil moisture and nutrient levels, optimizing water and fertilizer use. This can increase crop yields, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact.
- Energy Management: IoT can make energy systems more efficient, from smart grids that dynamically adjust to changes in energy demand to smart meters in homes that help consumers optimize their energy usage.
- Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization: IoT can streamline supply chains, with real-time tracking of goods and automated inventory management. This can lead to significant cost savings and increased efficiency in logistics.
- Enhanced Consumer Experiences: In retail, IoT can personalize shopping experiences, with smart shelves and interactive displays. In entertainment, immersive experiences can be created with connected devices.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: As more devices get connected, the potential for data breaches and privacy violations increases. Ensuring the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the data they transmit will be a major challenge.
- Job Market and Skill Shifts: IoT will create new job opportunities, particularly in fields like data analysis, network security, and IoT device development and maintenance. However, it may also render some jobs obsolete, necessitating a shift in workforce skills.
- Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability: IoT devices can monitor environmental conditions, helping in the fight against climate change by detecting forest fires early, tracking wildlife, and monitoring ocean health.
- Ethical and Legal Implications: The pervasive nature of Internet of Things (IoT) raises questions about surveillance, data ownership, and the ethical use of data. New legal frameworks may be required to address these issues.
- Global Connectivity and Digital Divide: While IoT has the potential to connect the world in unprecedented ways, it also risks exacerbating the digital divide. Regions with limited internet access may fall further behind, missing out on the benefits IoT can offer.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Transportation: Internet of Things (IoT) is a critical component in the development of autonomous vehicles. Connected cars, traffic lights, and road sensors can lead to safer, more efficient transportation systems. However, this also raises issues around infrastructure compatibility and safety regulations.
- Home Automation and Personal Assistants: Internet of Things (IoT) is making homes smarter and more efficient. From smart thermostats that learn user preferences to refrigerators that can order groceries, the possibilities are vast. Personal assistants powered by AI and IoT can manage and automate many aspects of daily life.
- Predictive Maintenance in Industries: IoT enables predictive maintenance in various industries. By monitoring equipment and predicting failures before they occur, companies can reduce downtime and save costs.
- Education and Learning: IoT can transform education, with connected devices providing personalized learning experiences and enabling remote learning opportunities. Interactive and immersive learning using IoT technologies can make education more engaging and accessible.
- Insurance and Risk Management: IoT devices can help in proactive risk management. For example, in the insurance industry, real-time data from connected devices can lead to more accurate risk assessments and tailored insurance policies.
- Interoperability and Standardization Challenges: As the number of IoT devices grows, ensuring they can communicate effectively becomes more challenging. Developing common standards and protocols will be crucial for maximizing the benefits Internet of Things (IoT).
- Emergence of New Business Models: IoT opens up new avenues for business innovation, including as-a-service models (like Lighting-as-a-Service in smart buildings) and data-driven decision-making strategies.
- Impact on Real Estate and Construction: Internet of Things (IoT) can significantly impact the real estate market, with smart building technologies offering more efficient building management, enhanced security, and improved energy efficiency, thereby changing the value proposition of buildings.
- Long-Term Sustainability and E-Waste: The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices raises concerns about electronic waste and the long-term sustainability of producing and discarding technology at such a rapid pace. Addressing these environmental impacts will be crucial.
Thank you for taking the time to read this post. We hope you found it informative and engaging. Would you like to stay updated. please don’t hesitate to get in touch.



